Fiery Engine Failure Caused by Metal Fatigue
This incident highlights the difficulty of subsurface flaw detection, and the limitations of modern inspection procedures.
Posted: February 20, 2018
By:
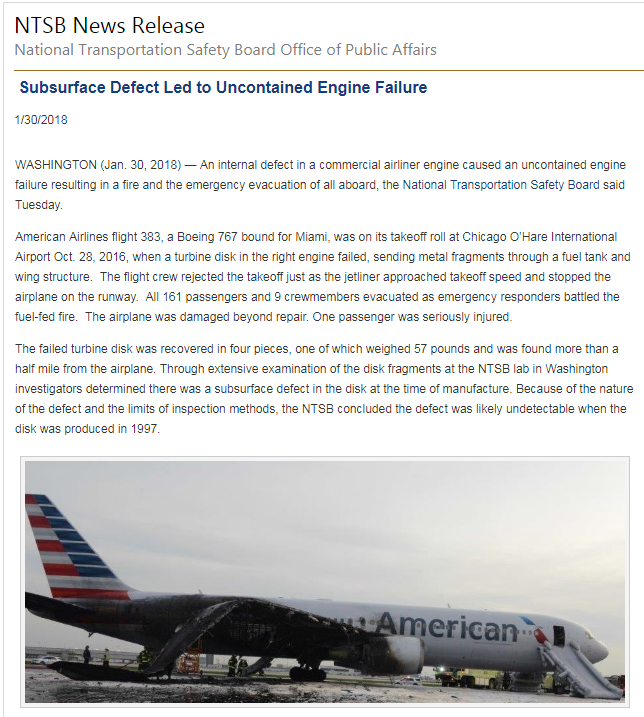
The National Transportation Safety Board (NTSB) released its report on a fiery engine failure that occurred at Chicago O’Hare International Airport in October, 2016. A high-pressure turbine disc ruptured as American Airlines Flight 383 accelerated down the runway, launching heavy fragments and debris up to half a mile away. Pilots aborted the takeoff and 170 people evacuated the aircraft as fire consumed the right engine and wing.
The NTSB attributes the failure to a subsurface defect in the nickel alloy turbine disc. The flaw likely originated during the manufacturing process but went unnoticed in subsequent inspections because it was so deep beneath the surface.
This incident highlights the difficulty of subsurface flaw detection, and the limitations of modern inspection procedures. Metal fatigue cracks can develop deep within a component, taking years to reach the surface and evading routine inspections. Laser Shock Peening offers a more proactive metal fatigue solution that inhibits fatigue cracking before it starts.
Laser peening generates deep compressive residual stresses which impede fatigue cracking and slow crack propagation. This compressive layer can extend several millimeters beneath the surface, providing robust protection at depths where inspection is difficult or unreliable. Engineers at Battelle Memorial Institute demonstrated this phenomenon decades ago while studying subsurface crack propagation in laser peened aluminum.
In an industry with no room for failure, aviation manufacturers are increasingly adopting Laser Peening to strengthen high-value components and prevent catastrophic failures. This powerful solution improves component safety and delivers major cost savings through lifestyle extension and maintenance reductions.
Prevention is always superior to inspection.
Stop fatigue cracking before it starts.
CONTACT LSPT TODAY.
Interested in Seeing More?
Tell us about your application, material, or failure mechanism and we will have one of our experts reach out to you. Our extensive library of research and years of experience gives us a unique advantage to apply a finite element analysis to help diagnose the best application for your situation.
